App Migration to the Cloud: Approaches and Difficulties
Common difficulties and main processes of migrating to the cloud?

What is cloud migration?
Cloud migration is the process of moving certain or all the enterprise data to the cloud-based infrastructure. For many businesses, app transferring is essential to operate more efficiently. In a long run, transferring an app optimizes expenses, and helps become more flexible and innovative. The most popular cloud solutions are offered by top-level providers like Azure, AWS, or GCP. Yet, the downsides of cloud migration are also significant. It costs a pretty penny and requires a point-by-point approach.
Common Challenges of Application Cloud Migration
End-to-end app migration to the cloud doesn’t happen in one go. It is a tricky process that requires substantial investments and time. Before making a final decision, you need to weigh all the pros and cons. The most important factor is the relevance of app migration to your business plans and needs. We share the common pitfalls to be avoided.
1. Outline the strategy
It is a typical mistake to begin the app migration process without dedicating ample time and focus on developing the strategy. An all-encompassing plan is essential for a successful migration. Every application may have various requirements and specifications. Hence, a unique approach to application cloud migration should be adopted. An understandable business case for every workload should be defined beforehand.
2. Data security
The app cloud migration process itself is risky, especially for huge amounts of data. Cloud service providers use a model of shared responsibility. It means they control infrastructure security while the customer deals with data and workloads protection. As a rule, cloud providers offer strong security measures and your task is to configure them precisely. You should identify and solve issues like data integrity corruption or security leaks immediately.
3. Transferring large databases
Attempting to migrate huge and complex databases via the Internet, you can face numerous obstacles. In this case, speed is the least important factor. Pay attention to all the processes to make sure that the system’s operation isn’t affected by the transfer. Some providers opt for physical methods. It means that the data is uploaded onto hardware and shipped to the cloud provider. For both ways of handling huge database migration, substantial time and attention are required.
4. Cost-efficiency
Unclear objectives and KPIs lead to an increased app migration budget. From the economic viewpoint, the expenditures may grow due to the adoption of new services and the growth of application usage. Aiming to reduce IT operational costs, many organizations expect to see instant results. Yet, they will be visible only after a certain time.
5. Switching providers
Switching cloud service providers is an expensive and time-consuming process. Many organizations start using cloud services from the first provider they come across. And when they find out that the current provider doesn’t meet their requirements, they need to change them. You need to keep in mind that with a huge variety of services from providers, only a few of them are extendable to other platforms. That’s why choose wisely first to avoid the difficulties for migration between different clouds.
6. Constant operation
Throughout the app migration process, the system’s operation should be uninterrupted. Overlap is necessary to ensure continuous operation. You may copy all the data before you shut down the actual database. Moving step by step is a wiser decision than trying to do everything at once when it comes to app migration.
6 Strategies to Migrate Apps to the Cloud
We would like to outline the main approaches to application migration called the 6 R's. To opt for the right strategy, consider all the critical business aspects and specifics.
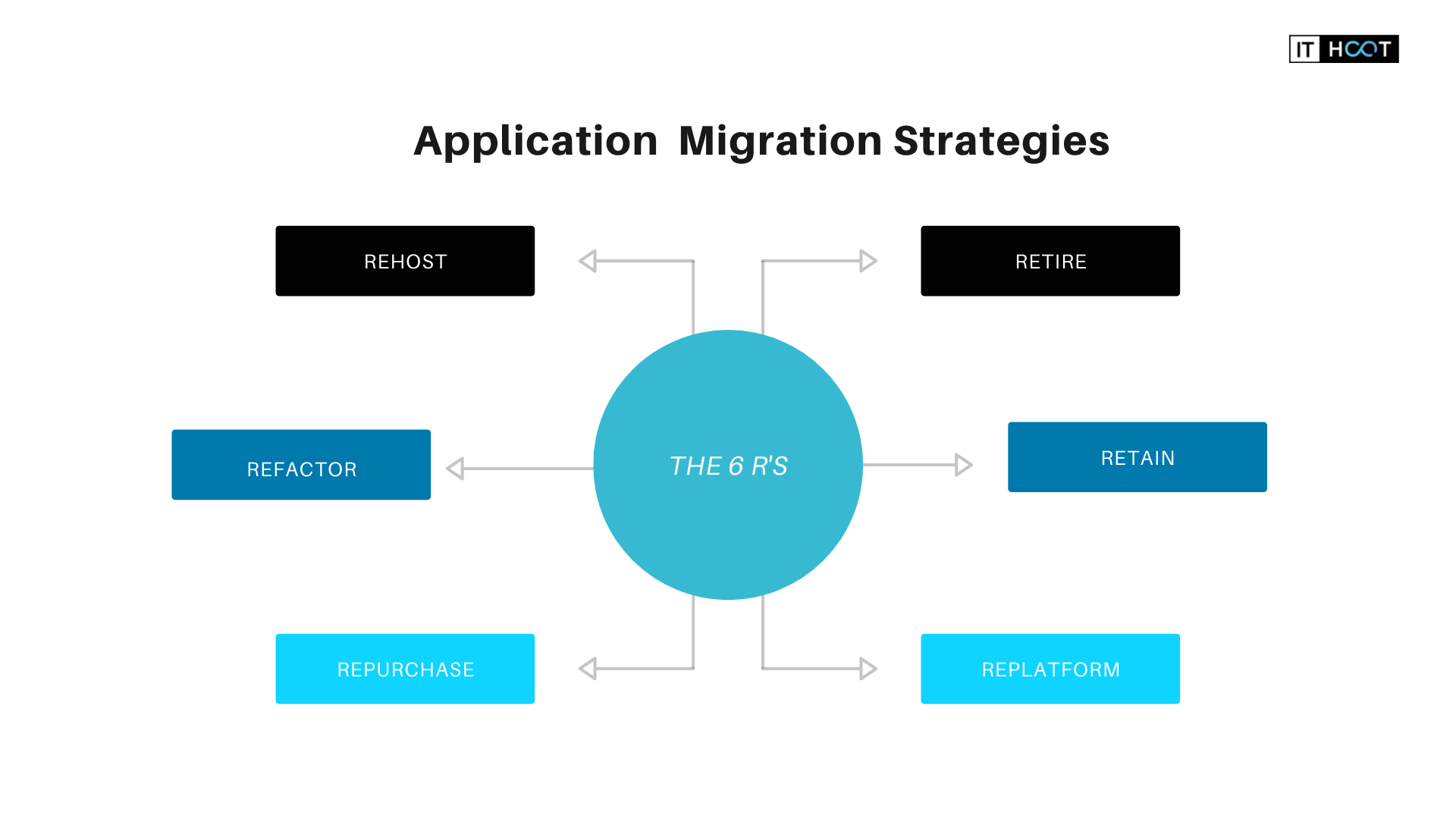
Rehost
Another name for this strategy is “lift and shift”. Rehosting is one of the easiest and fastest approaches you can automate with special tools like AWS VM Import/Export. In some cases, the client may require manual migration to learn how to use their new cloud system. The client can also optimize and adjust the architecture as the app is already functioning in the cloud.
Refactor/Re-Architect
This is an optimal approach if you need to scale, change, or upgrade the existing application. Refactoring reviews the existing architecture and replaces it with an optimal one for your business needs. This strategy implies rewriting the app from scratch to benefit from the cloud-native approach.
An example is a product transfer from a monolithic to a server-less architecture. The aim is to make it more flexible and enhance business productivity. As for the costs, this is the most demanding approach.
Replatform
Replatforming is a middle ground between the two methods we described above. It means rehosting an app to the cloud along with certain changes and enhancements to its functionality. It targets to make the most use of the new cloud architecture. Common changes involve modifying the program interaction with the database to make use of automation and flexible infrastructure. This approach optimizes costs and leverages cloud-native capabilities.
Repurchase
This strategy is also called “drop and shop”. It involves moving to a SaaS architecture while keeping all the capabilities of the existing product. Sometimes, you need to change the license of your on-premise provider to a cloud one. The cloud version of an app is more efficient, optimizes app storage and maintenance expenses. Repurchasing is suitable if you need to replace a CRM, CMS, or other software with a cloud-based solution. For instance, you decide to use Salesforce instead of on-premise CRM. This method enables speedy and effortless migration.
Retire
This approach means that an application or part of it is turned off. It makes sense when the organizations merge or go through acquisitions. Then, some functionality is no longer needed. Moreover, this approach helps reduce the system operational costs to 20%. It enhances your business operations and focuses your attention on the necessary things. Retiring reduces the surface areas for hacker attacks, which makes your solution more secure.
Retain/Revisit
If you are still having second thoughts about app cloud migration, retaining is an optimal choice. You don’t transfer an app to the cloud for now due to certain circumstances like lack of data, high costs, etc. You can put off this process and revise it when the circumstances or business needs change.
Main Deployment Methods for Cloud Migration
A deployment method is a certain configuration of environment parameters like storage size and accessibility. Deployment methods are defined by the location of the infrastructure for the environment.
Hybrid deployment
This approach implies combining data centers of different environments. With this method, you receive more flexibility. It is an optimal method for companies that require private clouds for sensitive data and public clouds with their advantages.
Multicloud deployment
This method employs using several cloud services within a single environment. Combining multiple cloud platforms provides more security and more space to store data.
Single cloud deployment
This is considered the easiest deployment method. Single cloud deployment is an ideal option for small companies needing only one cloud. However, it has the most limited results.
Wrapping Up
Migrating an application to the cloud doesn’t come without obstacles. We hope that our detailed guide gave you more insight into this process and helped avoid common mistakes.
A crucial factor for a successful migration is choosing a reliable provider of software migration services. You should look for a development team with extensive experience to migrate your application. IT Hoot engineers are ready to discuss the details and offer cost-effective and beneficial solutions.


